the-reclamation-cycle
The Reclamation Cycle: Tech Tree V0.1
Purpose: Define the starting tier buildings and resource trade-offs for the two core development paths: Restoration (Old World) vs. Adaptation (New World).
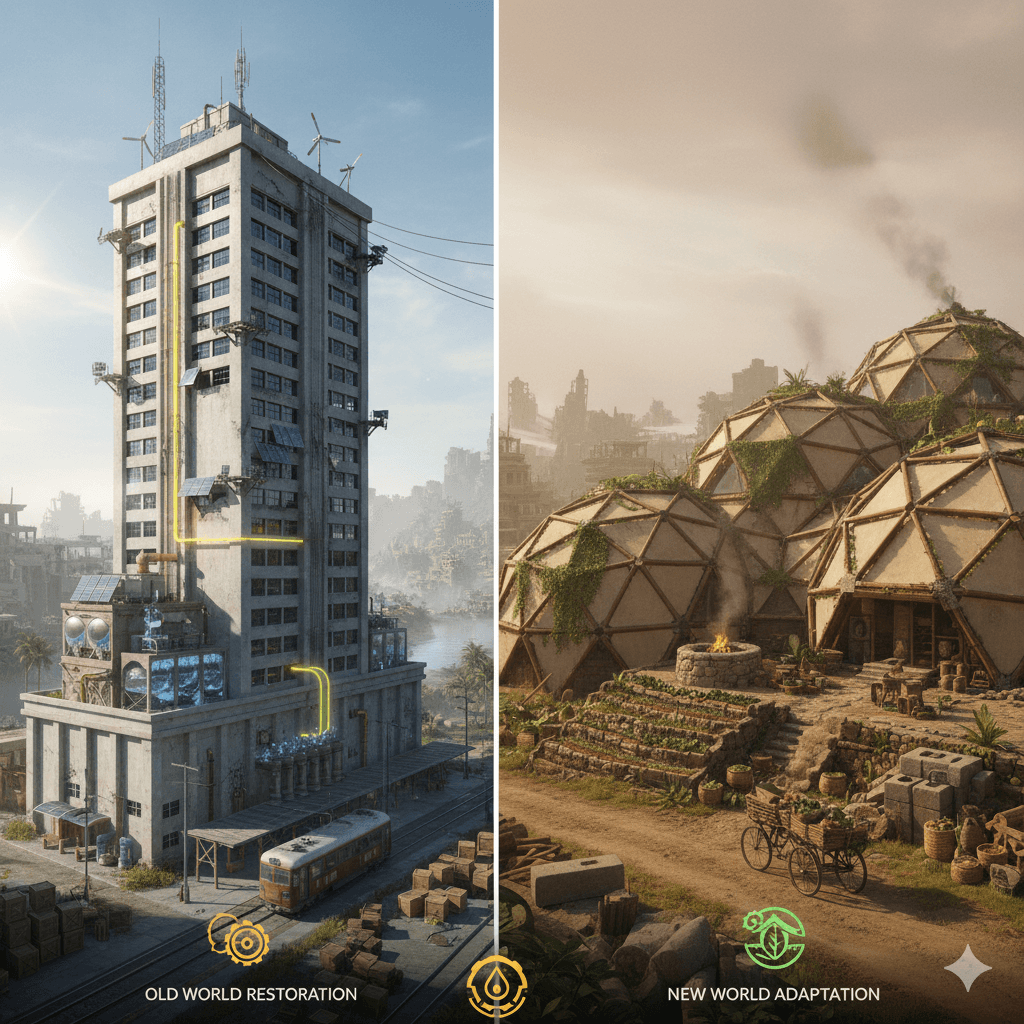
Strategic Choice: Restoration vs. Adaptation
Upon securing the initial settlement (Phase I), the player must commit to specializing in one of these two long-term philosophies. While some cross-pollination is possible, significant investment in one path locks out advanced research in the other.
1. The Restoration Path (Old World)
Goal: High population density, production efficiency, and automation. Trade-off: High initial investment in salvaged Core Components and high ongoing maintenance costs.
| Building / Tech | Unlock Requirement | Primary Resource Cost | Functional Benefit | Maintenance Burden |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete Aggregate Plant | Secured Electrical Generator | 200 Scrap Metal, 50 Motors | Processes rubble/sand into high-grade Concrete Aggregate. | High (Power, Water) |
| Automated Recycling Center | Advanced Scanners (Salvaged) | 150 Steel Rebar, 25 Electronic Kits | High-volume processing of junk into specialized Polymers/Wires. | Extreme (Specialized Kits) |
| Restored Water Pumping Station | Pumping Schematic | 300 Steel Rebar, 10 High-Pressure Pipes | Centralized, high-volume clean water supply. | High (Pipe Repair, Power) |
| Pre-Fab Housing Unit | Concrete Aggregate Plant | 50 Concrete Aggregate, 10 Steel Rebar | High-density housing for 50 people. | Medium (Water pressure dependent) |
| Narrow-Gauge Railbus | Restored Engine Blueprint | 5 Motors, 150 Scrap Metal | Fast, high-volume transport link between settlements. | High (Fuel, Track Repair) |
2. The Adaptation Path (New World)
Goal: Sustainability, resource resilience, and low maintenance. Trade-off: Lower production efficiency and lower population density per building.
| Building / Tech | Unlock Requirement | Primary Resource Cost | Functional Benefit | Maintenance Burden |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stone Masonry Workshop | Accessible Stone Quarry | 30 Wood Logs, 10 Tools | Processes raw stone into building blocks and mortar. | Low (Tools) |
| Biological Composting System | Waste Management Manual | 15 Wood Logs, 5 Fabric Rolls | Converts waste into Fertilizer and Biofuel (low volume). | Very Low (Manual Labor) |
| Decentralized Cistern & Well | Basic Water Filter | 50 Stone Blocks, 20 Wood Logs | Reliable, low-volume, local water supply. | Low (Filter replacement) |
| Tension-Fabric Shelters | Fabric Weaving Tech | 10 Wood Logs, 5 Fabric Rolls | Low-density housing for 20 people. | Medium (Fabric replacement) |
| Bicycle-Powered Hauler | Metalworking Tools | 2 Old Bicycle Frames, 10 Scrap Metal | Low-volume, zero-fuel transport route. | Very Low (Common parts) |
3. Core Component Dependencies (Examples)
Certain high-value salvaged items are critical and often non-renewable.
| Component | Found In (Salvage) | Used By (Examples) | Strategic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor | Wrecked Cars, Generators | Concrete Plant, Railbus, Restoration Tools | Essential for high-tier automation. |
| Electronic Kit | Server Rooms, Factories | Automated Recycling Center, Research Labs | Required for high-level Restoration research. |
| High-Pressure Pipe | Centralized Utility Tunnels | Restored Water Pumping Station | Required for large-scale water/sewage distribution. |
| Fabric Roll | Old Clothing Stores, Warehouses | Tension-Fabric Shelters, Composting Systems | Essential for all Adaptation path structures. |
4. Next Steps
- DOCS/Scenarios/Scenario_Contamination.md: Detail how the contamination event specifically impacts the salvage rate and maintenance cost of high-tech Old World components.